Basketry Techniques: Creating Sustainable Accessories with Natural Materials
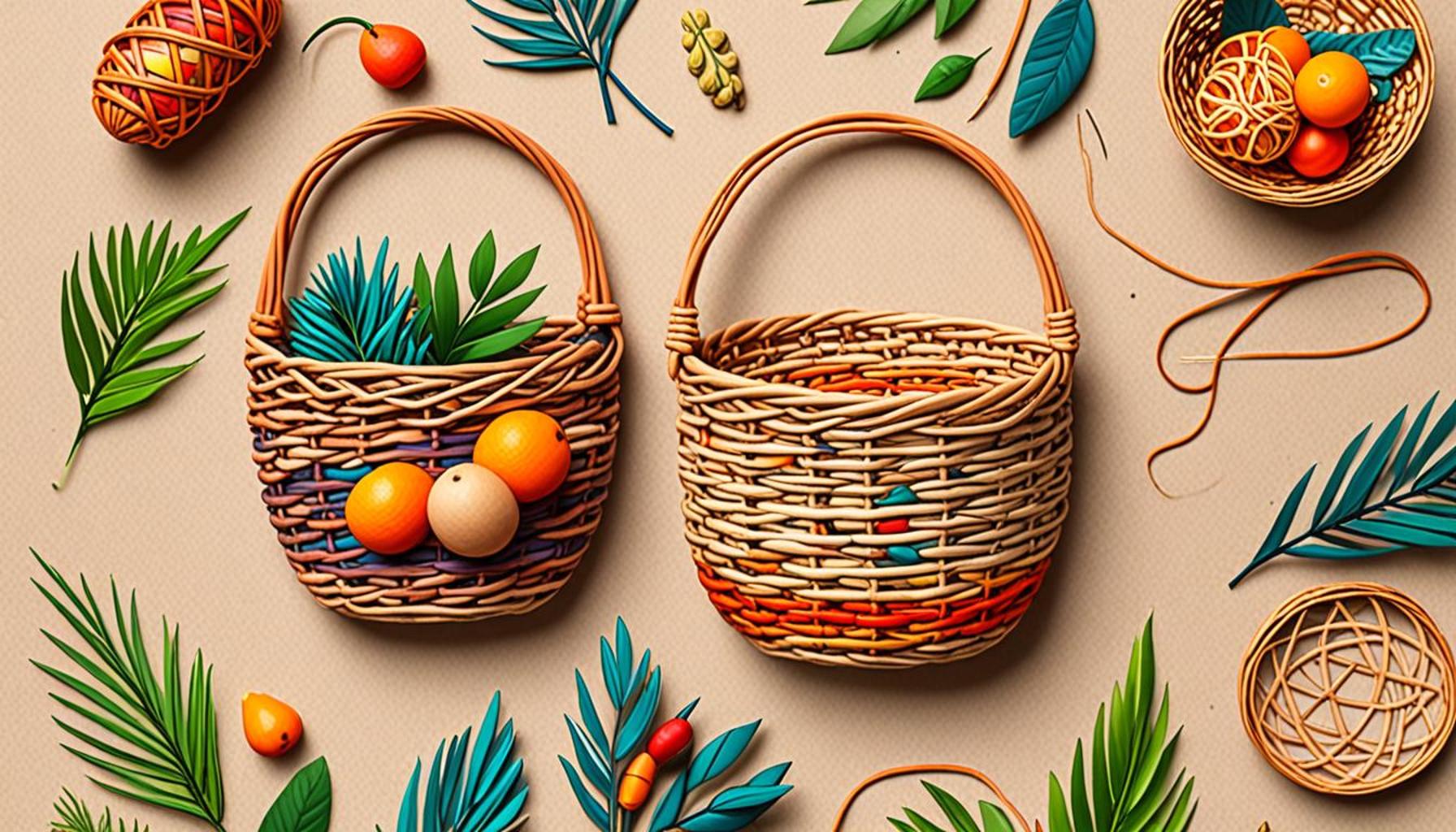

The Rich Heritage and Sustainability of Basketry
In our present times, where many are making conscious choices to prioritize sustainability, basketwork emerges as a captivating craft that harmonizes tradition with environmental responsibility. The roots of basketry reach far into the past, intricately woven into the cultural tapestries of different societies. This artisanal form of expression not only serves practical purposes but also symbolizes a deep respect for nature and heritage.
Across Nigeria, artisans create a plethora of stunning pieces utilizing local materials that echo the essence of their surroundings. This approach results in products that carry minimal ecological footprints while reflecting the skills and stories of their makers. The following aspects underscore the significance and beauty of sustainable basketry:
- Materials: Natural fibers such as rattan, raffia, and palm leaves provide the foundation for these creations. Rattan, for instance, is not only durable but also lightweight, making it ideal for various accessories. Raffia, sourced from the raffia palm, adds a unique texture and withstands various climates, allowing for both indoor and outdoor use.
- Techniques: Artisans employ various techniques including weaving, coiling, and twining. Weaving involves interlacing fibers to form a tight structure, while coiling uses spirals to create round shapes. Twining adds another layer of complexity and artistry, resulting in intricate designs that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
- Accessories: The range of items produced is impressive. From stylish bags and sun hats to decorative home pieces like wall hangings and baskets for storage, each item serves a practical purpose while elevating any space or outfit. For example, the popular “Akara” baskets, often used for storing food, showcase the beauty of traditional designs and craftsmanship while providing everyday utility.
Every basket is a story waiting to be told, a narrative of the land, culture, and the skilled hands that shaped it. By embracing these basketry techniques, we have an opportunity to redefine not just fashion and home décor but also our relationship with the environment. The choice of artisanal creations allows us to support local economies, preserving the ancient craft while promoting sustainability.
This article will explore the intricate world of basketry further, delving into the techniques used and the associated benefits. You will gain insights into how choosing handcrafted items can contribute positively to a more sustainable future, encouraging a shift towards eco-conscious living and celebrating the rich heritage of Nigerian artistry.
SEE ALSO: Click here to read another article
Exploring the Techniques of Sustainable Basketry
Basketry techniques have evolved through centuries of tradition, blending practicality with artistry to create functional items that resonate with environmental consciousness. In Nigeria, artisans master a range of methods that enhance the aesthetic and functional appeal of their creations while ensuring sustainability remains at the forefront. Understanding these techniques not only deepens our appreciation of this craft but also inspires us to incorporate sustainable practices into our daily lives.
Weaving, the most common technique employed by basket makers, involves the careful interlacing of materials to create robust structures. This method requires agility and precision, allowing artisans to craft intricate patterns that capture the eye and engage the spirit. The flexibility and strength of fibers like rattan lend themselves well to this technique, creating baskets that can withstand the wear and tear of daily use while retaining their charm.
Coiling is another prominent method where fibers are spiraled in a circular fashion, gradually building up to create sturdy forms. This technique offers versatility in shape, allowing artisans to create everything from flat, decorative pieces to rounded, deep baskets. The coiling technique not only showcases the artisan’s skill but also adds texture to the final product, making it ideal for both decorative and practical applications. For example, the colorful coiled baskets found in the northern regions of Nigeria reflect local traditions and are used for everything from storing agricultural produce to home décor.
Twining adds a layer of complexity to basket making through the intricate intertwining of two or more fibers. This method results in designs that are not only visually engaging but also structurally sound. Twined baskets are celebrated for their durability, making them a favored choice for carrying goods. The patterns created through twining can often symbolize community or family heritage, infusing each creation with cultural significance. Artisans in various regions use distinctive twining patterns that represent their unique backgrounds, fostering a sense of identity through their craft.
- Traditional Techniques: Many craftsmen adhere to age-old methods handed down through generations, ensuring that traditional skills are preserved. This not only offers a profitable livelihood to artisans but also empowers local communities.
- Innovative Methods: Some artisans blend contemporary techniques with traditional practices, experimenting with materials and designs that attract a modern consumer base. This innovation opens new avenues for income while maintaining an eco-friendly approach.
- Collaborative Initiatives: Various communities have taken proactive steps to form cooperatives, pooling resources and skills to enhance their basketry production and market reach, ensuring sustainability is at the core of their operations.
By delving into these fascinating techniques of basketry, we unlock the potential not only for sustainable fashion but also for cultivating a deeper connection with our environment. Embracing these artisanal products means acknowledging their cultural significance and supporting local economies, fostering an ecosystem where traditional craftsmanship thrives alongside modern sustainability efforts. As we examine the methods of these skilled artisans, we find an inspiring model for creating sustainable accessories that stand the test of time.
| Category | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Eco-Friendly Materials | Utilizing natural materials reduces plastic waste and promotes environmental sustainability. |
| Cultural Heritage | Preserving traditional basketry techniques supports local artisans and keeps cultural practices alive. |
| Customization | Natural materials offer a unique aesthetic that can be personalized according to individual taste. |
| Durability | Sustainable accessories made from natural fibers often outperform synthetic alternatives in longevity. |
In the exploration of Basketry Techniques, we uncover a realm where functionality meets artistry in the creation of sustainable accessories. Each category listed illustrates not only the practicality but also the deep-rooted traditions associated with basket weaving. These time-honored methods are more than just artistic expressions; they embody the principles of eco-friendliness, ensuring that our choices today enhance our planet for future generations. Embracing these techniques allows individuals to partake in a much-needed movement towards sustainability while supporting artisans who carry the knowledge of these valuable skills. The result is a collection of beautiful, functional items that speak volumes of our commitment to a greener lifestyle. As awareness of the importance of natural materials grows, so too does an interest in learning these techniques, drawing enthusiasts closer to the heart of crafting sustainable accessories with purpose and style.
CHECK OUT: Click here to explore more
Natural Materials: The Heart of Sustainable Basketry
The essence of sustainable basketry lies in the natural materials chosen by artisans. Traditionally, basket makers have relied on locally sourced fibers, which reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation and manufacturing. Natural materials such as palm fronds, grasses, reeds, and sisal are favored for their versatility, availability, and durability. For instance, the use of palm fibers in the southern and southeastern regions of Nigeria reflects both the environmental conditions and the cultural heritage of these areas.
Palm fronds, harvested sustainably from palm trees, are often handwoven into intricate patterns that not only showcase skilled craftsmanship but also serve as a statement against synthetic alternatives. Additionally, the process of gathering these fibers exemplifies community engagement, as families often work together to collect, prepare, and weave these materials. This communal approach fosters a sense of solidarity while ensuring that sustainable practices are upheld.
Another significant material, reeds, are often used in the production of baskets in Niger state. Artisans expertly manage the harvesting cycles, allowing reeds to regenerate, which demonstrates a commitment to environmental conservation. The basketry products created from reeds range from functional storage solutions to exquisite decorative items, each item telling a story about the interconnectedness of the people and their natural surroundings.
Color and Texture in Basketry
Beyond functionality, artisans in Nigeria embrace the aesthetic potential of these natural materials to create visually stunning pieces. The incorporation of dyes derived from local plants and minerals adds a vibrant palette to the baskets, transforming them into art pieces. For example, artisans in the southwestern regions use natural plant extracts to dye their baskets, achieving a spectrum of colors that reflect the rich biodiversity of the Nigerian landscape.
The textural variations achieved through different weaving techniques contribute to the tactile experience of the baskets. A coiled basket might contrast sharply with a twined one, providing layers of interest in both touch and sight. Artisans often utilize stitching techniques that allow for the embedding of beads or other embellishments, further enhancing the aesthetic allure of their work while maintaining its sustainable nature.
Preserving Cultural Heritage Through Basketry
Another pivotal aspect of sustainable basketry in Nigeria is its role in preserving cultural heritage. Each region boasts its own historical context and traditional crafts that are deeply woven into the cultural fabric. For example, the Fulani communities have long been associated with distinctive weaving styles, while the Yoruba and Igbo peoples infuse their baskets with local motifs that tell tales of historical significance. This cultural storytelling not only enriches the items produced but also fosters a sense of pride among artisans and recipients alike.
Furthermore, as the global demand for ethical and sustainable products grows, the potential for basketry as a viable economic enterprise expands. Artisans are increasingly trained in business skills and marketing, allowing them to reach broader markets while preserving their traditional crafts. Collaborative platforms, local cooperatives, and exhibitions allow these artists to showcase their work, connecting the age-old techniques of basketry with contemporary sustainability narratives.
As artisans weave together strands of tradition with innovative approaches to material use and design, they present a powerful model for crafting sustainable accessories. Navigating the intersection of culture, art, and environmental consciousness, these craftsmen not only supply practical items but also foster a movement that positions sustainability at its core.
ADDITIONAL INSIGHTS: Expand your understanding here
Conclusion: The Future of Basketry as Sustainable Art
The journey through the rich tapestry of basketry techniques in Nigeria reveals an intriguing intersection of art, culture, and sustainability. By harnessing natural materials like palm fronds and reeds, artisans not only create beautiful accessories but also uphold environmental principles that resonate deeply in today’s eco-conscious market. The communal spirit highlighted in the crafting process fosters both resilience and solidarity among communities, ensuring that tradition thrives alongside innovation.
Moreover, the incorporation of colors derived from local plant dyes enriches the aesthetic appeal of baskets, transforming functional items into captivating art pieces that reflect the country’s diverse biodiversity. As artisans continue to preserve cultural heritage through unique weaving styles and motifs, they invite consumers to reconnect with the stories and histories embedded within each piece.
As the demand for ethically produced products rises globally, the potential for sustainable basketry grows stronger, creating economic opportunities for artisans. This shift not only supports the livelihood of the craftspeople but encourages a greater appreciation for eco-friendly practices. By choosing sustainable accessories, consumers play a pivotal role in fostering this movement, ultimately contributing to the preservation of both culture and the environment.
As we look ahead, it is essential to support these artisans and their craft, allowing the vibrant world of sustainable basketry to flourish. Engaging with these practices offers an opportunity for individuals to explore deeper connections with nature and culture, all while adorning themselves with unique handmade accessories that symbolize a commitment to sustainability.


